When a diesel engine turning over but not starting, it can be particularly frustrating when essential equipment or vehicles are urgently needed. Understanding common engine fault causes and solutions can help us respond quickly in critical situations, preventing issues from worsening.
In this post, we will delve into the reasons why diesel engines sometimes won’t start, discuss specific repair measures, and provide preventive tips to reduce the likelihood of similar issues in the future. Let’s get started!
Part 1. Common Causes of Diesel Engine Turning Over but Not Starting
Diesel engines use a unique compression-ignition process, unlike gasoline engines that require a spark plug. This difference presents specific issues when the engine doesn’t start, even when it’s cranking. These are some common causes of the diesel engine cranking but not starting.
1. Fuel System Issues
A diesel engine requires fuel continuously to sustain combustion. When fuel isn’t reaching the cylinders properly, the engine will crank without starting. Common fuel system issues include:
- Air in the Fuel Lines: Air bubbles in the fuel line can disrupt the fuel flow, leading to starting problems.
- Fuel Filter Blockages: A blocked fuel filter can prevent fuel from reaching the engine, leading to a no-start scenario.
- Fuel Pump Failure: If the fuel pump is weak or broken, fuel won’t reach the injectors, preventing the engine from starting.
2. Battery Problems
While diesel engines don’t rely on spark plugs, they still require a powerful battery to start the engine. If the battery voltage is too low, the engine may run but not start. Common battery-related issues include:
- Low Battery Charge: A weak battery charge can result in a slow or ineffective crank.
- Faulty Battery Connections: Corrosion or loose battery terminals can disrupt the power flow to the engine.
3. Glow Plug Malfunction
In cold weather, glow plugs play a crucial role in warming up the diesel engine for combustion. When glow plugs are faulty, the engine may run but won’t start, particularly in low temperatures.
4. Compression Problems
Diesel engines need high compression to ignite fuel-air mixture. If there is a compression problem, such as worn pistons, rings, or valves, the engine may fail to start.
5. Faulty Sensors or ECM (Engine Control Module)
Modern diesel engines use sensors and the ECM to control fuel injection timing, air intake, and other crucial functions. Faulty sensors can cause incorrect signals to be sent to the ECM, causing starting issues.
Part 2. How to Troubleshoot Diesel Engine Crank But Not Starting?
As we’ve mentioned potential reasons previously, now it’s time to know how to diagnose and fix each problem.
1. Fuel System Diagnosis
To diagnose fuel system issues, start by checking the fuel lines for leaks or air pockets.
- Check for Air in the Lines: If you find air bubbles, bleed the fuel system according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Inspect and Replace Fuel Filters: If your filter appears dirty or clogged, replace it. Regularly make filter changes to avoid future issues.
- Test the Fuel Pump: Use a multimeter to check the voltage that reaches the fuel pump. If the pump is faulty, replace it.
2. Battery and Electrical System Check
If the battery is the likely cause:
- Measure the Battery Voltage: Use a multimeter to check the battery. A fully charged battery should read around 12.6 volts.
- Clean Battery Terminals: If there is corrosion present, clean the terminals with a wire brush and reconnect them.
- Inspect Wiring: Check the wiring between the battery and the starter for any loose connections.
3. Glow Plug Inspection
For problems related to glow plugs:
- Test Glow Plug Resistance: Use a multimeter to measure the resistance. A reading outside the specified range indicates a faulty plug.
- Replacing Faulty Glow Plugs: If the glow plugs are worn or old, replace them to restore cold starting reliability.

4. Compression Testing
To identify potential compression issues:
- Use a Compression Tester: A compression test will determine if the engine meets the required pressure levels.
- Check Piston Rings or Valves: Low compression could indicate worn rings or valve issues, requiring professional inspection or engine rebuilding.
5. Sensor and ECM Diagnostic
For modern diesel engines:
- Check Engine Codes: Use a diagnostic tool to scan for error codes, which can indicate sensor or ECM issues.
- Replace Faulty Sensors: If sensors such as the crankshaft or camshaft sensor are causing problems, replace them to restore proper engine function.
Part 3. Tips to Avoid Future Diesel Engine Starting Problems
Regular preventive maintenance can significantly reduce the risk of your diesel engine cranking without starting. Here are some tips on maintaining your engine’s performance:
Regular Fuel Filter Replacement: Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for changing the fuel filters.
Battery Maintenance: Clean the terminals, check the voltage regularly, and replace the battery as needed.
Glow Plug Testing: Test glow plugs annually, especially in colder weather.
Engine Inspections: Regular inspections of the engine and its components can help identify problems before they become serious.

Part 4. Alternative Starting Solution: Spring Starter for Diesel Engines
Diesel engines can encounter various types of issues, with “turning over but not starting” being just one of them. When starting problems arise, having a reliable backup solution is crucial.
Although a spring starter can’t directly resolve the “turning over but not starting” issue, it can provide an effective backup option, especially in remote or harsh environments where electric starting systems may be unreliable. This ensures the diesel engine can start up smoothly when needed.
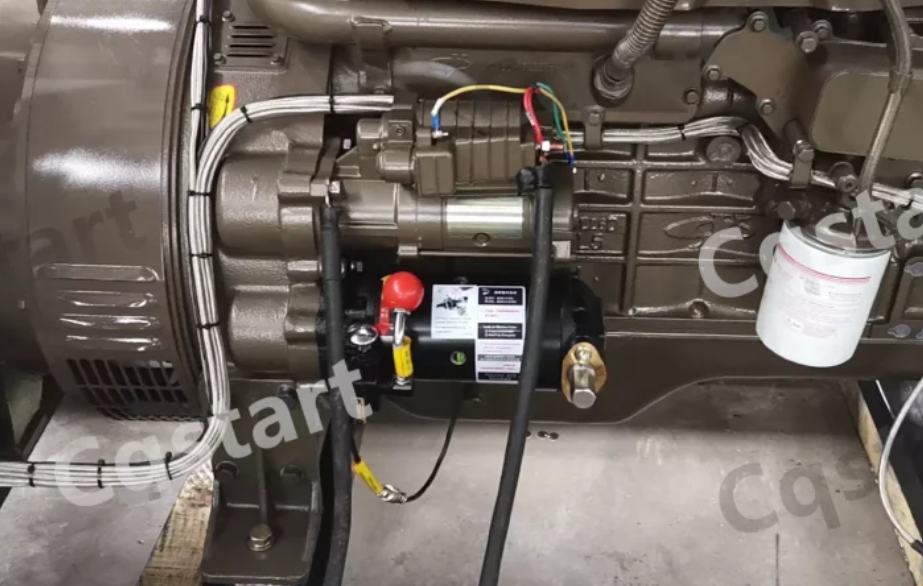

What is a Spring Starter?
A spring starter is a manually wound device that stores energy in a high-tension spring. Upon release, it provides the necessary power to start the engine without relying on a battery or electrical system. This type of starter is particularly useful in environments with:
Battery Drain Risks: Such as in extreme weather or when battery replacements are expensive.
Remote Locations: Where engine reliability is crucial, and electrical power may not always be available.
Harsh Environments: Where equipment is frequently subjected to vibrations, dirt, and extreme temperatures, resulting in faster battery wear.
By using a spring starter, operators have a reliable backup method to start their engines when traditional electrical systems fail, ensuring they are not stranded in challenging conditions.
In a Word
When your diesel engine turns over but won’t start, you can follow these troubleshooting steps to identify and address potential issues effectively. If you’ve tried various methods and still encounter starting problems, it’s best to seek assistance from a professional mechanic.
Furthermore, having a backup solution for the diesel engine is crucial for enhancing its reliability. For instance, Cqstart spring starter provides stable starting support across various environments, helping ensure your diesel engine starts smoothly.
FAQs about Diesel Engine Starting
1. Why wont my diesel engine start even with starting fluid?
If your diesel engine won’t start even with starting fluid, it may be due to issues beyond fuel ignition. Common causes include low compression, faulty fuel injectors, or a malfunctioning glow plug system, which are all crucial for the diesel engine’s combustion process.
Starting fluid only aids in ignition but cannot overcome these mechanical issues. Additionally, repeatedly using starting fluid on diesel engines can cause damage, so it’s best to check for these underlying issues.
2. How do you force start a diesel engine?
To force-start a diesel engine, first ensure the battery is fully charged and fuel is reaching the injectors. In cold weather, use glow plugs or block heaters to warm the engine, as diesel engines require heat for combustion. You can also try starting the diesel engine with a spring starter.
3. What is the life of the engine of a diesel generator?
The lifespan of a diesel generator engine typically ranges from 10,000 to 30,000 hours, depending on factors such as maintenance, operating conditions, and load consistency.
With regular maintenance and optimal operating conditions, such as avoiding overloading and allowing sufficient cooling time, a diesel generator can last for many years. High-quality models and well-maintained engines can even surpass this range, providing reliable performance for decades.
4. Can diesel generators run nonstop?
Diesel generators can run continuously for extended periods if maintained properly, but require regular refueling, oil changes, and cooling to prevent overheating. For long-term non-stop operation, it’s crucial to schedule shutdowns for servicing to ensure efficiency and avoid potential damage.

