Diesel engines are the backbone of modern transportation and heavy machinery, widely used in trucks, ships, and construction equipment. Understanding how does a diesel engine start is crucial for operators.
In this post, we will delve into relevant information about diesel engines, including common starting problems and their solutions, to help you use diesel engines more effectively, increasing your efficiency and convenience.
Part 1. What is Diesel Engine?
What is diesel engine? Diesel engine is an internal combustion engine that primarily generates power by compressing air to ignite diesel fuel. Unlike gasoline engines, diesel engines do not rely on spark plugs; instead, they use high-pressure compression to raise the air temperature, causing the diesel fuel to ignite spontaneously at high temperatures.
Diesel engines are commonly used in trucks, ships, construction equipment, and generators, and offer higher fuel efficiency and torque output. Their design enables them to perform exceptionally well in heavy loads and extended operating periods.
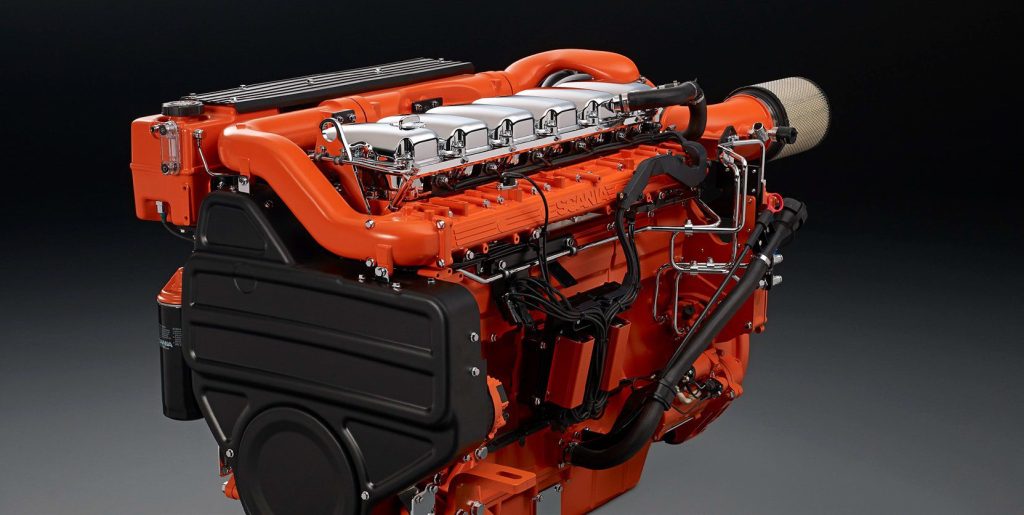

Part 2. Essential Parts of Diesel Engine
Diesel engine is a complex system composed of multiple key components, each performing unique functions that work together to achieve efficient power generation.
Every component plays a crucial role in operation, ensuring smooth and efficient operation under various conditions. Let’s take a closer look at its components.
Fuel System
Fuel system in a diesel engine is essential for delivering diesel fuel from the tank to the combustion chamber, ensuring efficient combustion and optimal performance.
It includes:
- Fuel tank
- Fuel pump
- Fuel filters
- Fuel lines
- Fuel injectors
The system works by drawing fuel from the tank, filtering out impurities, and delivering it at the correct pressure to the injectors, which atomize and inject fuel into the combustion chamber for ignition. Advanced systems, such as common rail injection, provide precise control over fuel delivery, improving efficiency and reducing emissions.
Lubrication System
Lubrication system in a diesel engine is vital for reducing friction and wear among the moving parts, ensuring smooth operation, and extending the engine’s lifespan.
It includes:
- Oil pump
- Oil filter
- Oil sump
- Oil passages
Oil pump circulates lubricant from the oil sump through the engine, delivering it to critical areas such as the crankshaft, pistons, and camshaft. The oil filter removes impurities from the oil, maintaining its purity and effectiveness.
The system provides adequate lubrication to minimize heat buildup, reduce friction, and protect against wear, ultimately contributing to the engine’s efficiency and reliability.
Air Intake System
Air intake system in a diesel engine is crucial for ensuring a steady supply of clean air for the combustion process.
It includes:
- Air filter
- Intake manifold
- Turbocharger
It works by drawing air from the environment through the air filter, which removes dust and contaminants to protect the engine. The filtered air then enters the intake manifold and is distributed evenly to the cylinders.
In turbocharged engines, a turbocharger compresses the incoming air, increasing its density, allowing for a greater amount of air-fuel mixture, which enhances combustion efficiency and power output.

Exhaust System
Exhaust system in a diesel engine is designed to safely and efficiently expel combustion gases from the engine while minimizing emissions and noise.
It includes:
- Exhaust manifold
- Catalytic converter
- Diesel particulate filter (DPF)
- Muffler
The exhaust manifold collects gases from the cylinders and directs them into the exhaust system. The catalytic converter reduces harmful emissions by converting pollutants into less harmful substances, while the DPF captures soot and particulates to prevent them from entering the atmosphere.
Finally, the muffler helps reduce noise produced by the engine’s exhaust gases. Together, these components ensure that the diesel engine operates efficiently and quietly while adhering to environmental regulations.
Cooling System
Cooling system in a diesel engine is essential for maintaining optimal operating temperatures and preventing overheating.
It includes:
- Radiator
- Water pump
- Thermostat
- Coolant passages
Water pump circulates coolant through the engine, absorbing heat generated during combustion. The coolant then flows to the radiator, where it is cooled by air before being returned to the engine. The thermostat regulates the flow of coolant based on the engine’s temperature, ensuring that the engine operates within an efficient temperature range.
An effective cooling system not only enhances engine performance and longevity, but also helps prevent potential damage caused by excessive heat. Regular maintenance of the cooling system is crucial for ensuring reliable engine operation.
Electrical Systems
Electrical system in a diesel engine plays a vital role in starting the engine and powering various components necessary for operation.
It includes:
- Battery
- Alternator
- Starter motor
- Sensors
- Control modules
The battery provides the initial electrical power to start the engine, while the starter motor cranks the engine to initiate the combustion process. Once the engine is running, the alternator generates electricity to recharge the battery and provide power to the electrical systems, including lights, instrumentation, and fuel injectors.
Additionally, sensors monitor various parameters such as temperature, pressure, and engine speed, which are then fed to the engine control unit (ECU) to improve performance and efficiency. A functioning electrical system is crucial for the efficient operation of a diesel engine.
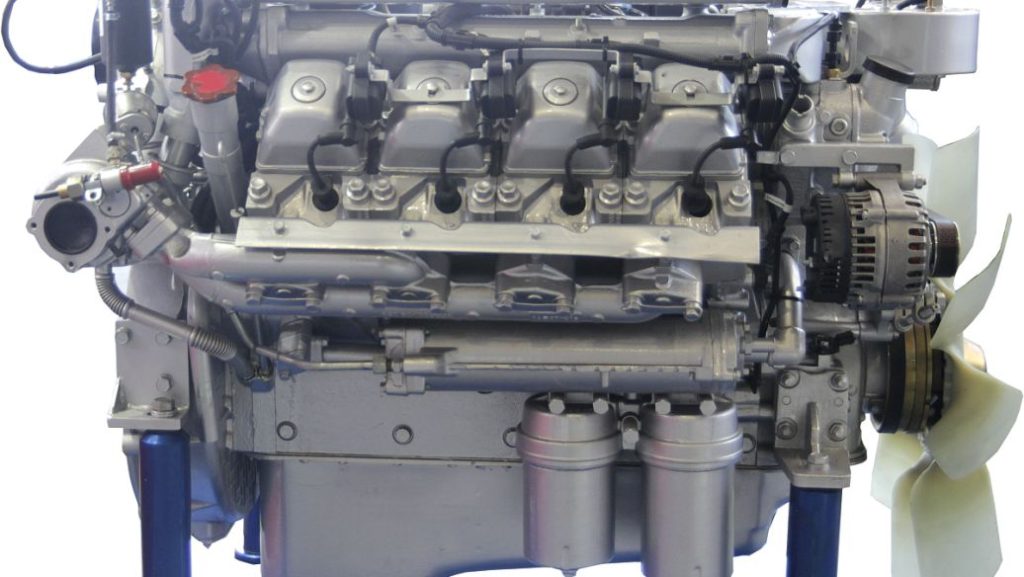

Part 3. How Does a Diesel Engine Start?
Starting a diesel engine involves several key steps, here’s how does a diesel engine typically work:
First, turning on the ignition key activates the battery, providing power to the starter motor, which begins to turn the engine. At this point, the intake valves open, allowing in outside air to be drawn into the cylinders.
Next, the piston moves upward, compressing the air within the cylinder, causing the temperature to rise. Just before reaching the top dead center, the fuel injector sprays diesel into the high-temperature compressed air, igniting spontaneously.
Then, combustion generates high-pressure gases that push the piston downward, driving the crankshaft to complete the starting process.
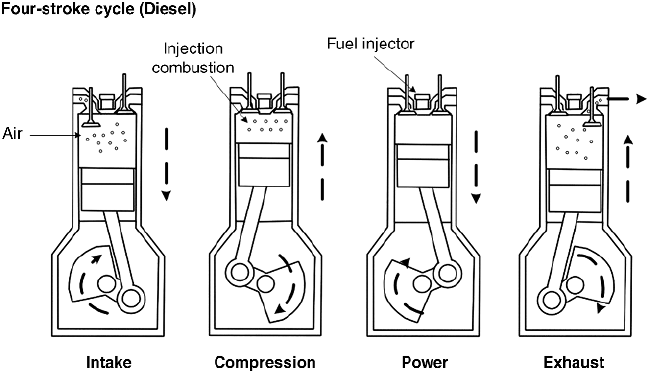
How Does a Diesel Engine Turn Fuel into Power?
A diesel engine typically operates by repeating a cycle of four stages, or strokes. This four-stroke cycle utilizes the intake, compression, combustion, and exhaust processes to efficiently convert fuel into power.
Air Intake: The engine draws in ambient air through the intake manifold as the piston moves down during the intake stroke.
Compression: As the piston moves up, it compresses the air in the cylinder, significantly increasing its temperature due to the high compression ratio typical in diesel engines(14:1 to 25:1).
Power Stroke: The force from the combustion pushes the piston downward, converting the energy from the burning fuel into mechanical energy. This downward movement turns the crankshaft, generating power.
Exhaust: After the power stroke, the piston moves back up to expel the exhaust gases through the open exhaust valves, completing the cycle.
Part 4. What Factors Impact Diesel Engine Start?
Temperature: Low temperatures can cause diesel fuel to become viscous, leading to poor fuel injection and affecting combustion efficiency. In extremely cold weather, diesel may even freeze, further hindering engine startup.
Battery: Diesel engines require a strong battery charge to operate the starter motor. Aging or insufficient battery power can prevent the starter motor from turning properly, making it impossible to start the engine. Additionally, battery connections that are corroded or loosened may result in inadequate current.
Fuel Quality: Poor-quality fuel may contain water, impurities, or additives that negatively impact combustion performance and the proper functioning of fuel injectors. Water can cause fuel emulsification, reducing combustion efficiency and potentially damaging engine components.
Engine Condition: Internal wear, poor sealing, or aging components can affect the compression ratio and combustion efficiency of the engine. Damage to the cylinder head gasket or wear on the piston rings can lead to compression leaks, making starting more difficult.
Part 5. Practical Tips for Starting a Diesel Engine with Ease
Multiple factors can cause difficulties starting a diesel engine, which can be a significant concern for users. To improve the start-up performance, we can adopt some effective methods. Here, we will provide some practical tips to help you start your diesel engine with ease.
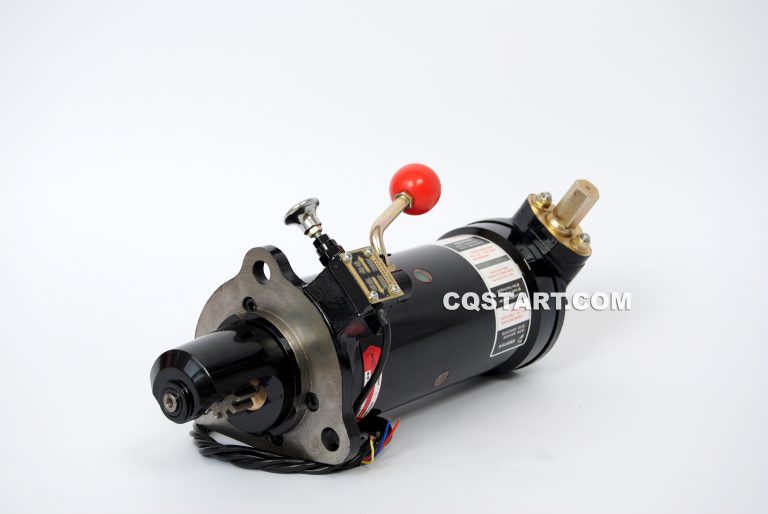
1. Using Spring Starter
When a diesel engine has difficulty starting, using a spring starter can enhance the smoothness of startup. Spring starter is ideal for operating in extreme temperatures or high-load conditions, as it can quickly and steadily deliver power to the engine.
This method not only improves starting efficiency but also reduces reliance on the battery, reducing the risk of startup failure. Therefore, spring starter can be an ideal choice for improving the performance of diesel engines.

2. Battery Maintenance
Regularly checking the battery’s charge and connection status is crucial for ensuring the smooth startup of a diesel engine. Check the battery voltage to ensure it is fully charged and make sure the connections are secure to prevent corrosion that can lead to insufficient current.
To enhance startup reliability, replace aging batteries promptly and keep the surface clean. Furthermore, in cases of low power, consider using a spring starter to assist with startup.
3. Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance is crucial for ensuring efficient engine operation. To maintain lubrication, change the oil and check and replace the air and fuel filters. Regularly check the fuel system, including the injectors and fuel pumps, to avoid supply issues. These measures can extend the engine’s lifespan and enhance its starting performance and efficiency.
4. Monitoring Engine Condition
Regularly inspecting key components such as cylinder seals, piston rings, and valves is crucial for ensuring smooth engine startup. The good condition of these parts ensures proper sealing and an appropriate compression ratio, helping to prevent startup difficulties.
A well-sealed cylinder prevents gas leakage, while worn piston rings can negatively impact engine power and starting performance. Therefore, replacing damaged components and checking the condition of the cooling and lubrication systems can enhance the overall performance and reliability of the engine.
5. Choose High-Quality Fuel
Using high-quality diesel fuel is essential for ensuring smooth engine startup and efficient operation. High-quality fuel has fewer water and impurities, which can improve combustion efficiency and prevent incomplete combustion and damage to the injectors.
This not only improves starting performance but also reduces carbon buildup and emissions, contributing to a longer engine lifespan. Hence, it’s crucial to select reputable suppliers and regularly monitor fuel quality.
Summary
The startup process of a diesel engine is complex and precise, involving the coordinated operation of multiple steps and components. However, in daily operations, there may be instances where the diesel engine fails to start. In such cases, spring starter can be a reliable solution for starting diesel engine. Additionally, regular inspections and maintenance are crucial for ensuring the long-term reliability of the diesel engine.

